
Kar Chun Tan
Creator
Metadata
What is Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)?
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) allows developers to run a Linux environment directly on Windows, without the overhead of a traditional virtual machine or dual-boot setup.
There are two versions of WSL:
- WSL 1: An compatibility layer for translating Linux system calls (syscalls) to Windows ones.
- WSL 2: A full linux kernel running in a lightweight virtual machine, offering better performance, full system call compatibility, and full Docker support.
I highly recommend using WSL 2 for most use cases due to its improved performance and compatibility and it is the default version when installing WSL.
Installation & Setup
Before you begin, ensure that your Windows 10 version is 2004 or higher (Build 19041 or higher) or you’re using Windows 11. Else, you can refer to the official documentation for manual installation steps.
Enable WSL Feature
Basically, you can enable and install WSL with a single command. Open PowerShell in Administrator mode and run the following command:
wsl --install
wsl --install -d <Distro> # To install a specific distributionThis command does everything for you:
- Enables the required “Windows Subsystem for Linux” optional feature.
- Enables the “Virtual Machine Platform” optional feature.
- Downloads and installs the Ubuntu Linux distribution by default.
- Sets WSL 2 as the default version for any new Linux distributions installed.
Restart your computer when prompted [Optional]
In most cases, the above command will not require a restart. However, if the wsl --install command fails, you may need to manually enable the features and restart your computer.
Go to your Start Menu, search for “Turn Windows features on or off”, and enable the following features:
- Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Virtual Machine Platform
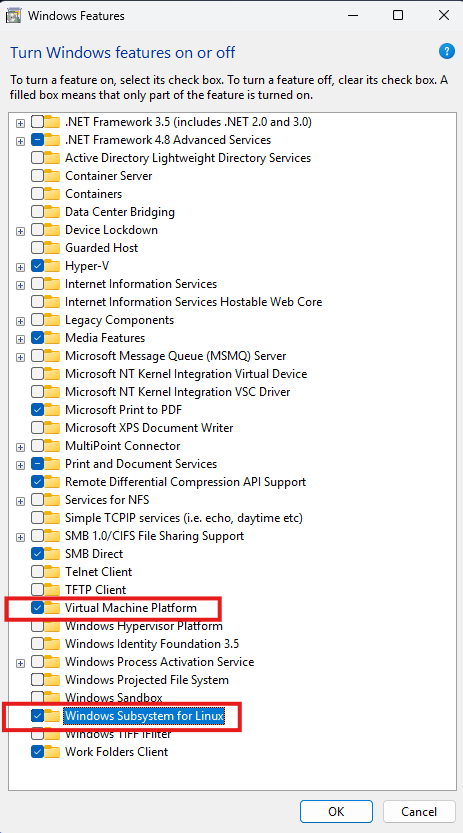
After enabling these features, restart your computer to apply the changes.
Initial Setup of your Linux Distro
After you done all the steps correctly, you will see a new “Ubuntu” application in your Start Menu. Launch it and a terminal window will open. It will take a few minutes to set itself up.
- The username can be anything you like
- It is recommended to use a lowercase name without spaces or special characters
- It will be your default user for the Linux environment
- It will be the administrator for the Linux environment (sudo user)
After that, you will be prompted to enter a new UNIX username and password. Basically, this user account is your default user for the Linux environment and is separate from your Windows user account.
Also, make sure to remember the password you set here, as you will need it for executing commands with sudo privileges. Once you have completed these steps, you will be logged into your new Ubuntu terminal.
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Install the latest PowerShell for new features and improvements! https://aka.ms/PSWindows
PS C:\Users\karchunt> wsl --install
Downloading: Ubuntu
Installing: Ubuntu
Distribution successfully installed. It can be launched via 'wsl.exe -d Ubuntu'
Launching Ubuntu...
Provisioning the new WSL instance Ubuntu
This might take a while...
Create a default Unix user account: karchunt
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
karchunt@DESKTOP-CCAQ09F:/mnt/c/Users/karchunt$Basic WSL Management Commands
Let’s go through some basic WSL management commands that you might find useful.
List available Linux distributions
This command wil list all the Linux distributions that are available for installation via WSL through the online store.
wsl -l -o
wsl --list --onlinePS C:\Users\karchunt\Desktop\All\karchunt.com> wsl -l -o
The following is a list of valid distributions that can be installed.
Install using 'wsl.exe --install <Distro>'.
NAME FRIENDLY NAME
AlmaLinux-8 AlmaLinux OS 8
AlmaLinux-9 AlmaLinux OS 9
AlmaLinux-Kitten-10 AlmaLinux OS Kitten 10
AlmaLinux-10 AlmaLinux OS 10
Debian Debian GNU/Linux
FedoraLinux-43 Fedora Linux 43
FedoraLinux-42 Fedora Linux 42
SUSE-Linux-Enterprise-15-SP6 SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP6
SUSE-Linux-Enterprise-15-SP7 SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP7
Ubuntu Ubuntu
Ubuntu-24.04 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
archlinux Arch Linux
kali-linux Kali Linux Rolling
openSUSE-Tumbleweed openSUSE Tumbleweed
openSUSE-Leap-16.0 openSUSE Leap 16.0
Ubuntu-20.04 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Ubuntu-22.04 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
OracleLinux_7_9 Oracle Linux 7.9
OracleLinux_8_10 Oracle Linux 8.10
OracleLinux_9_5 Oracle Linux 9.5
openSUSE-Leap-15.6 openSUSE Leap 15.6List installed Linux distributions
This command will list all your installed distros and their current status.
wsl -l -v
wsl --list --verbosePS C:\Users\karchunt\Desktop\All\karchunt.com> wsl -l -v
NAME STATE VERSION
* Ubuntu-24.04 Stopped 2
Ubuntu Stopped 2
docker-desktop Stopped 2Set a Specific Distro to use WSL 1 or WSL 2
This command allows you to change the WSL version for a specific installed distribution.
wsl --set-version <distribution-name> <wsl-version>
wsl --set-version Ubuntu-24.04 2Set WSL 2 as the Default Version
This command allows you to set the default WSL version for any new Linux distributions that you install in the future.
wsl --set-default-version <version>
wsl --set-default-version 2Set default Linux distribution
This command allows you to set the default Linux distribution that will be used when you run wsl without any arguments.
wsl --set-default <distribution-name>
wsl --set-default Ubuntu-24.04Terminate a running Distro
This command allows you to terminate a specific running WSL distribution.
wsl --terminate <distribution-name>Shutdown WSL (All Distros)
This command allows you to shut down all running WSL distributions. This is useful if you want to free up system resources or if you need to restart WSL for any reason.
wsl --shutdownCore WSL Usage & File System
Accessing Windows Files from WSL
WSL automatically mounts your Windows drives under the /mnt directory. For example, your C: drive is accessible at /mnt/c.
You can try to cd into your Windows user directory using wsl terminal:
karchunt@DESKTOP-CCAQ09F:/mnt/c/Users/karchunt$or using WSL command line
wsl cd /mnt/c/Users/karchunt
wsl ls -la
wsl pwdRunning a Windows Executable from WSL
You can run Windows executables directly from your WSL terminal. For example, to open Notepad, you can simply type:
notepad.exe <file>
# or
explorer.exe <path>WSL Configuration (.wslconfig)
You can configure global WSL settings using a .wslconfig file located in your Windows user profile directory (e.g., C:\Users\<YourUsername>\.wslconfig).
Here is an example of a .wslconfig file:
[wsl2]
memory=4GB # Limits VM memory to 4 GB
processors=2 # Limits VM to 2 processors
swap=2GB # Sets swap file size to 2 GB
swapFile=C:\\temp\\wsl_swap.vhdx # Custom swap file location
localhostForwarding=true # Enables localhost forwardingAfter creating or modifying the .wslconfig file, you need to shut down WSL for the changes to take effect:
wsl --shutdown